WHAT IS BIOGAS
Biogas is a Gaseous green renewable energy resource obtained from the anaerobic fermentation of biodegradable matter which can be waste obtained from agricultural sector, municipal sector and food sector. It is composed of Methane, Carbon dioxide, Hydrogen sulfide and other trace gases, the exact composition varies based on the feed stock and the production pathway.

WHY BIOGAS
Biogas is the ultimate solution for multifaceted challenges in present era like
- It acts as an Alternative sustainable solution to Greenhouse gas effects like methane emissions on environment.
- It acts as a viable energy substitute for Fossil fuels, in reducing carbon footprint and mitigating the climate change.
- It converts the organic waste to clean energy and minimizes the waste accumulation in landfills.
- The byproduct in the Biogas production acts as the nutrient rich fertilizer for sustainable agricultural practices and eventually decreasing the usage of synthetic fertilizers.
HOW BIOGAS IS PRODUCED
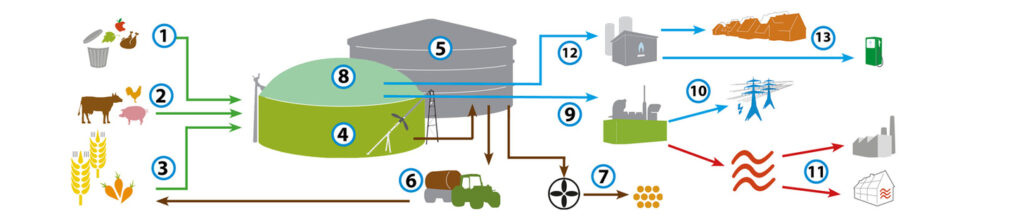
- Biogas feed sources:
Food and Agriculture waste, Animal and Municipal solid waste, Waste water sludge are collected and prepared and sometimes chopped and shredded to make it easily digested.
Few feedstock sources from different sectors:
Agriculture sector | Agriculture residues like cereal grain straws, corn stover, dried leaves, stalks etc Energy crops like maize, sweet sorghum, barley can be source of biomass for biogas. |
Dairy sector | Dairy manure and Poultry litter |
Municipality sector | Municipal solid waste like organic waste from households, restaurants, super markets |
Food Industry | Bakery waste like waste bread, doughnuts, dough waste etc. and unsold cereal origin products Brewery waste like fruit pulps, brewing slop, left over and fermented waste called trub and water waste Sea food processing waste Waste from vegetable canning, potatoes processing, sugarcane production. |
Industry | Industrial residues, effluents and waste water from paper industry, pharmaceutical industry, distillery and so on |
Oil mill | Palm oil, sunflower oil mill effluents |
Ethanol production | Press mud from ethanol refineries |
Slaughter houses | Left over and unused parts of meat |
Sewage plants | Urban and rural sewage sludge from septic tanks and waste water effluents. |
Forestry | Branches, barks and tree residues after logging operations. Dead wood and dried leaves. |
2. Anaerobic Digestion in the Biodigesters:
After pretreatment like grinding, mixing and heating, the material is now transferred to the fermenters / digesters with oxygen free environment where the microbes like methanobacteria act upon it and converts into biogas.Mesophilic degradation requires 38-40˚c and thermophilic degradation requires 50- 60˚c.
Types of digesters:
- Continuous stirred tank Reactor in which there is a continuous process of input of feed stock and biogas collection from their respective input and output areas under continuous stirring condition.
- Upflow Anaerobic Sludge blanket reactor in which the feedstock flows upwards through a bed of sludge in anaerobic environment.
- Plug flow reactor in which the feed stock moves in horizontal or cylindrical tubes in one direction without constant mixing.
Types of digestion:
- WET DIGESTION: Water is used to mix with the feedstock and it is suitable for small-scale biogas production plants.
- SEMI-DRY DIGESTION: This method uses feedstock with moderate moisture content and requires less water than wet digestion. It is suitable for medium to large-scale biogas plants and offers a balance between process efficiency and water usage.
- DRY DIGESTION: Here the dry feedstock is fermented in fermenter boxes with liquid digestate or percolate sprinkled on the dry mass. This method is suitable for large-scale production.
3. Biogas collection and Purification:
Obtained Raw biogas is collected on top of the digesters and collected through pipes and purified to remove moisture, hydrogen sulfide, carbon dioxide and siloxanes to convert into clean and renewable natural gas known as Biomethane.
Steps involved in Purification of Biogas are known as Biogas Scrubbing.
Removal of carbon dioxide | 1. Water scrubbing: Biogas is passed through water under high pressure and carbon dioxide gets dissolved in water whereas methane is left over in the biogas. 2. Pressure Swing Adsorption: In this, adsorbent materials like Zeolites and Activated carbon are used to adsorb carbon and concentrate methane in Biogas. 3. Membrane Separation: Selective permeable hollow fiber gas separation membranes which retains methane and allow carbon dioxide to pass through it. 4. Chemical Absorption/Amine scrubbing: Monoethanolamine, MEA solution is used to absorb carbon dioxide and later heated to regenerate the solution. |
Removal of Hydrogen sulfide | 1. Chemical Scrubbing ( FE & EDTA based) Biogas is passed through a bed of iron oxide, Hydrogen sulfide reacts with iron oxide to form iron sulfide. 2. Wet Scrubbing Biogas is passed through a tower filled with sodium hydroxide or potassium hydroxide solution in which hydrogen sulfide gets absorbed. 3. Dry Scrubbing 4. Bio-scrubbing Micro organisms are used to degrade hydrogen sulfide in bioreactors. |
Moisture (H₂O) Removal | Dehumidifier / Heat Exchanger |
4. Biogas storage and Analyzation:
Biogas is stored in inflated bags, fixed dome storage, long flexible horizontal tubes also in cylinders.
Online integrated gas analyzers are used to continuously measure and display the obtained Gas composition to ensure safety of the equipment and to prevent contamination and enhance the production of energy efficiently.
Technology used in these analyzers are:
- Infrared spectroscopy: Analyses gases like methane and carbon dioxide based on the IR absorption patterns.
- Thermal conductivity: Based on the amount of heat conduction, analyzes the quantities of methane and carbon dioxide gases.
- Electrochemical sensors: A current proportional to the hydrogen sulfide and oxygen gas concentrations are generated upon chemical reactions.
- Catalytic combustion sensors: Flammable gases are analyzed such as Methane.
- Photoionization detectors: Detects gases like siloxanes and preventing damage to the equipment.
5. Compression and filling unit:
The obtained Biomethane is compressed with the help of multi stage compressors at a pressure of 250 bar hence called as Compressed Bio Gas (CBG).
This CBG is stored in high pressure storage tanks made of high strength stainless steel material, ready to be dispensed called as cascades.
The filling stations uses specialized refueling equipment like pressure regulated dispensers to ensure safe and accurate filling into the fuel tank of the vehicles.
WHERE IS BIOGAS USED
- Electricity generation (Power Plants)
- Fuel: a sustainable energy source both for cooking and transportation replacing fossil fuels.
GOVERNMENT INITIATIVES:
- Central sector schemes under Ministry of New and Renewable Energy are
| 1. New National Biogas and Organic Manure Programme (NNBMOP) | |||||
| Plant size | 1cu.m. to 25 cu.m. per day | ||||
| Eligibility |
50-60 sqm area for installing small biogas plant. Regular availability of feedstock and water supply Financial capacity to invest their share. |
||||
| Central subsidy rates state wise and depending on the area of plant | 1m3 | 2-6m3 | 8-10m3 | 15m3 | 20-25m3 |
| NER including Sikkim, SC/ST of NER | 17000 | 22000 | 24000 | 25000 | 35000 |
| Special category states and SC/ST of all states | 10000 | 13000 | 18000 | 21000 | 28000 |
| General category of all states | 7500 | 12000 | 16000 | 20000 | 25000 |
| Cattle dung based Biogas plant linked with sanitary toilets in individual house get additional incentives in rupees | 1600 | 1600 | 1600 | NIL | NIL |
| 2. Biogas power generation and thermal energy production scheme (BPGTP) | |
| Plant size | 30 m3 to 2500 m3 |
| Power generation Capacity Range | 3Kw to 250Kw |
| Eligibility | · State Renewable Energy Agencies · Biogas development and Training Centers · Khadi and Village Industries Commission · National Dairy Development Board · State Agriculture and State Rural Development Departments. |
| Financial Assistance | After successful completion and commissioning of the project, Financial assistance is Reimbursed. |
| Plant size 1-25m3/day | 9800-70,400 Rs per plant based on its size |
| Power generation for 25-2500 m3 per day | 35000-45000 Rs per Kilowatt power generated |
| Thermal power plant capacity of 25-2500 m3/ day | 17500 – 22500 Rs per Kilowatt equivalent |
| For NER, island, Registered Gaushalas and SC/ST beneficiaries | Avail 20% higher CFA than Standard CFA as in the above scheme |
3. SWACHH BHARAT MISSION (GRAMIN 2.0) – WASTE TO WEALTH MISSION
Government of India launched this scheme under the Ministry of Jal Shakti on October 2,2020 to ensure Open Defecation Free Rural India. It is the Upgraded version of the Swachh Bharath Mission Grameen 1.0.
Its Comprehensive approach is Sustainable management of Solid and liquid waste.
Central Financial Assistance Will be provided to Gram panchayats and Urban Municipalities for setting up Biogas plants and Waste to energy Initiatives.
4. NATIONAL BIOENERGY PROGRAMME -WASTE TO ENERGY PROGRAMME:
Under the Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE) for a period of 1-4-2021 to 31-3-2026, with a fund allocation of Rs 858 crore under phase -1.
SUB-SCHEMES are
WASTE TO ENERGY PROGRAMME | 2021-22 to 2025-26 CFA available for setting up of large Biogas, BioCNG, Power plants. SATAT (Sustainable Alternative Towards Affordable Transportation) under Ministry of Petroleum and Natural Gas aims 15MMT of CBG from 5000 plants. |
BIOMASS PROGRAMME | CFA is available for Setting up of Pellets and briquettes Manufacturing units, and Non-bagasse based power generation projects |
BIOGAS PROGRAMME | 2021-22 to 2025-26 Financial assistance for setting up of Biogas plants from 1-2500m3 biogas per day |
Write Service related Content

